In this blog we will be seeing everything about useEffect Hook in ReactJs.
UseEffect Hook
The useEffect hook is a fundamental feature in React that allows you to perform side effects in functional components. Side effects are actions that your component might need to perform that aren't directly related to rendering. These can include data fetching, subscriptions, DOM manipulations, and more. The useEffect hook is designed to address the challenges of managing side effects in React components.
What is UseEffect Hook Used for?
Data Fetching:
- Use
useEffectto fetch data from APIs or external sources after the component mounts or when certain dependencies change.
- Use
DOM Manipulation:
- Perform DOM manipulations, such as adding or removing elements, updating styles, or interacting with third-party libraries, within the
useEffectfunction.
- Perform DOM manipulations, such as adding or removing elements, updating styles, or interacting with third-party libraries, within the
Subscriptions:
- Set up subscriptions to events or data streams, such as web sockets, and manage them using
useEffect. Don't forget to clean up the subscription when the component unmounts.
- Set up subscriptions to events or data streams, such as web sockets, and manage them using
Updating Document Title:
- Utilize
useEffectto update the document title based on the component's state or props.
- Utilize
Timers and Intervals:
- Use
useEffectto start and manage timers or intervals, ensuring they are cleared when the component unmounts to prevent memory leaks.
- Use
Conditional Effects:
- Conditionally apply effects based on certain conditions or props, allowing you to control when the effect should be executed.
Side Effects on Component Updates:
- Run side effects when specific props or state variables change, by providing those dependencies in the dependency array of
useEffect.
- Run side effects when specific props or state variables change, by providing those dependencies in the dependency array of
Effect Cleanup:
- Return a cleanup function from
useEffectto handle resource cleanup, such as unsubscribing from events or cancelling pending requests.
- Return a cleanup function from
Local Storage Interaction:
- Use
useEffectto interact withlocalStorageorsessionStoragewhen you need to synchronize component state with browser storage.
- Use
Global State Updates:
- Use
useEffectto trigger global state updates in state management libraries like Redux or MobX.
- Use
Animating Components:
- Manage animations with
useEffectby applying styles or classes to elements and controlling their timing.
- Manage animations with
Handling Document Events:
- Attach event listeners to the
documentwithinuseEffectto handle global events like clicks or key presses.
- Attach event listeners to the
Code Splitting and Lazy Loading:
- Use
useEffectto trigger dynamic imports for code splitting and lazy loading of components.
- Use
Tracking Analytics:
- Use
useEffectto send analytics data or track user interactions to external services.
- Use
Custom Hooks:
- Build custom hooks that encapsulate specific side effect logic, promoting code reusability and maintaining clean components.
Server-Side Rendering (SSR) Compatibility:
- Use
useEffectwith caution in server-side rendered applications to ensure client-side and server-side rendering behavior align.
- Use
Parts of UseEffect Hook
The useEffect hook in React consists of a few key components that work together to manage side effects in functional components. Let's break down the parts of the useEffect hook:
Effect Function: This is the core part of the
useEffecthook. It's a function that contains the code you want to run as a side effect. The effect function will be executed after every render of the component. It can include tasks like data fetching, DOM manipulation, setting up subscriptions, or anything that involves interacting with the outside world.Example:

Dependency Array: The dependency array is an optional second argument of the
useEffecthook. It's an array that specifies the dependencies that the effect function relies on. If any of the dependencies change between renders, the effect function will be re-executed. If the dependency array is omitted, the effect function will run after every render.Example with dependencies:

Effect Cleanup Function: Inside the effect function, you can optionally return a cleanup function. This function will be called before the next render or when the component unmounts. It's commonly used to clean up resources like event listeners, timers, or subscriptions to prevent memory leaks.
Example with cleanup:

Implementation of UseEffect Hook
To understand the implementation of useEffect Hook we will be making a api call using useEffect Hook.
Step 1: Importing the necessary Hooks from react

Step 2: Creating two States, one for
Dataand other forloadingstate
Step 3: Creating a useEffect for fetching data form
json placeholder apithen converting it intojsonand then setting it intoData Stateand setting theLoading Statetofalseso that we can display the data from the API Response.
Step 4: Now we will display
user idanduser namefrom the response by mapping through the data and then we will be displaying the data in theli tag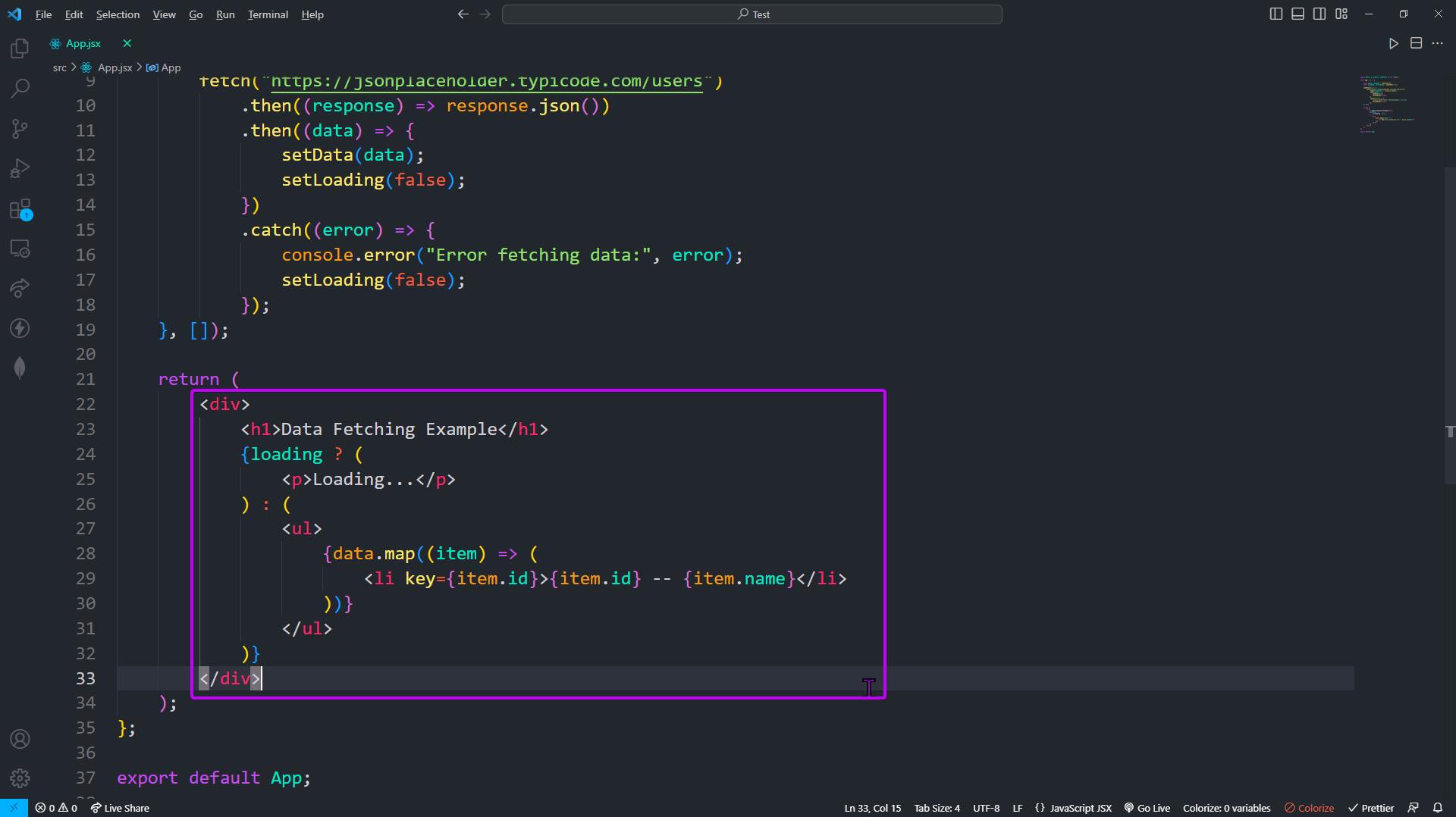
Step 5: For Final Output we will the below command
npm start
So, in this blog, we learned about UseState Hook in ReactJS, State Management, Ways of managing states in react, useState Hook in react and Implementation of useState Hook in react. There is much more to learn about UseEffect Hook in ReactJS, explore this topic and its used cases and elevate your skills.
Adios Amigos 👋👋
